Teach Students To Be Global Citizens With These 5 Strategies
28th August 2023

As classrooms become increasingly diverse and the world grows more interconnected, teaching students how to be good global citizens is no longer optional, it is a necessary part of modern education. Whether students live in busy metropolitan areas or small rural communities, their lives are shaped by global events, shared resources, and collective challenges such as climate change, inequality, and technological advancements.
Many educators ask, “What is global citizenship?”
In simple terms, global citizenship is a mindset and way of living that recognizes our shared humanity. It means understanding global citizen meaning beyond academics — embracing empathy, cultural awareness, responsibility, and a willingness to contribute positively to the world.
UNESCO defines global citizenship education as an approach that helps learners develop the knowledge, values, and skills they need to participate in a peaceful, inclusive, and sustainable world.
Let’s explore the traits of global citizens, along with practical global citizenship activities for students that teachers can use today.
What Is Global Citizenship?
Global citizenship is more than a concept, it is a mindset, a skillset, and a way of engaging with the world. It teaches learners to recognize that they are part of an interconnected global community where actions in one part of the world can influence people, environments, and systems elsewhere.
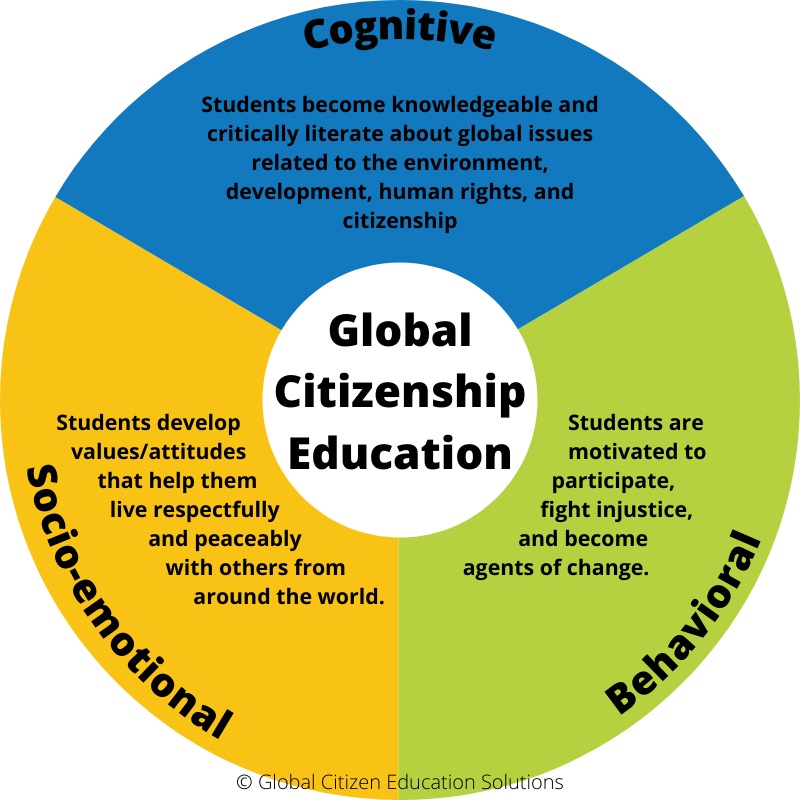
A global citizen is someone who:
- Understands global interconnectedness — How economies, cultures, ecosystems, and technologies influence one another.
- Respects cultural diversity — Valuing differences in traditions, beliefs, and perspectives.
- Thinks critically about world issues — Climate change, conflict, inequality, digital safety, sustainability.
- Takes responsible action — Contributing to positive change locally and globally.
- Acts with empathy and humanity — Recognizing that all people share equal dignity and rights.
In simple terms, the global citizen meaning goes beyond nationality. It’s about thinking globally and acting responsibly. Global citizens are adaptable, informed, compassionate, and solution-oriented, qualities that help students thrive in an ever-changing world.
Key Characteristics & Responsibilities of a Global Citizen
Students who embrace global citizenship typically develop:
- Inclusivity – Valuing all cultures and identities
- Awareness of global issues – Climate change, Equality, Humanitarian needs
- Cultural intelligence – Understanding perspectives different from their own
- Critical thinking – Analyzing global problems with clarity
- Solution-oriented mindset – Finding responsible ways to take action
- Empathy & humanity – Caring about global well-being
These characteristics form the responsibilities of a global citizen, helping young people become informed, ethical, and active contributors to society.
5 Ways to Prepare Students for Global Citizenship
Changing students' mind is not a task that can be completed overnight. It is a slow but evident process and teachers can see the change in their students in the way they make their decisions, treat people, or approach problems. Educators must be mindful of the fact that these children will be responsible citizens one day and hence while focusing on their holistic growth; they must also teach them to be global citizens to increase their chances of succeeding in the world.
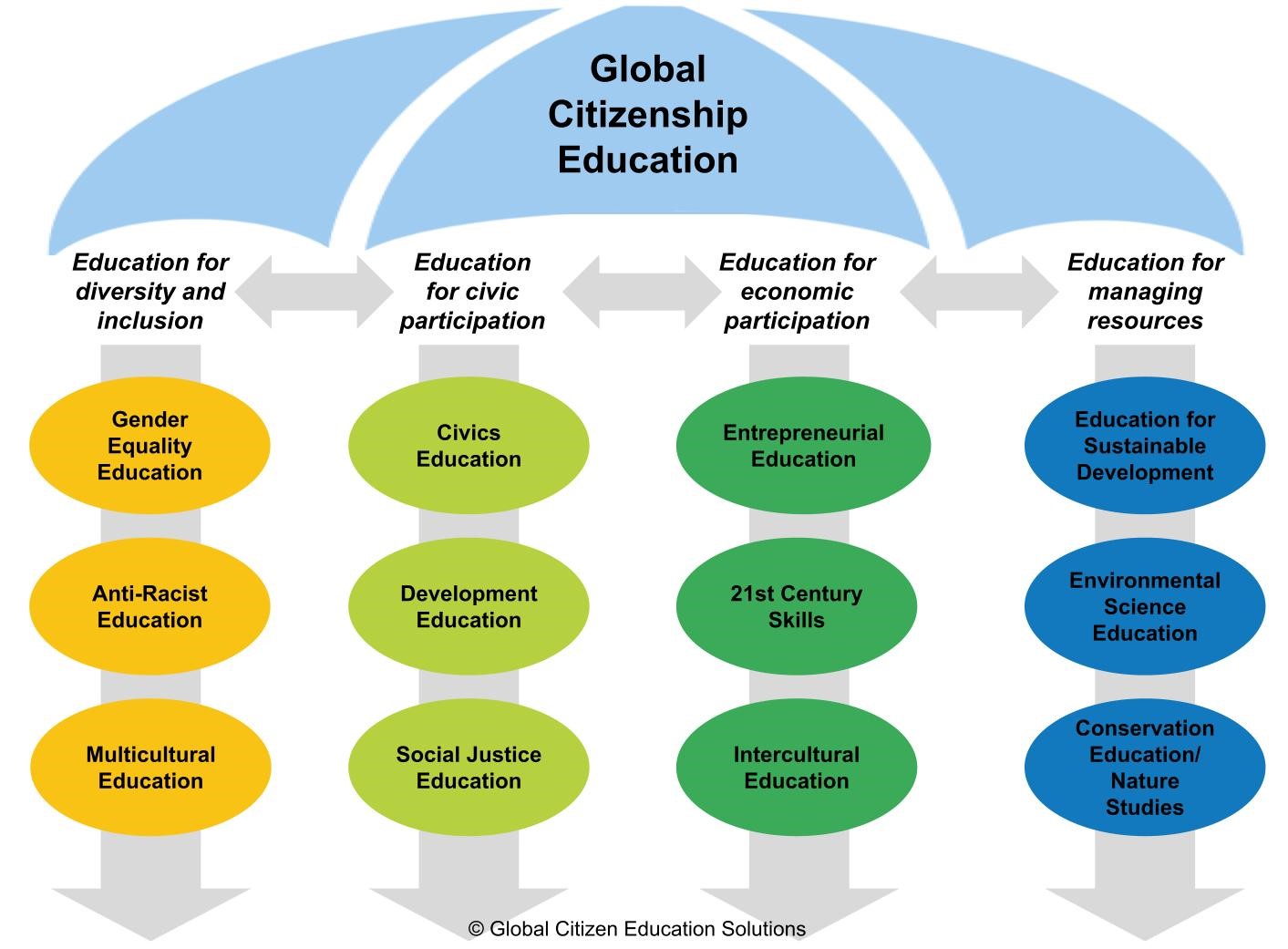
Here are 5 essential ways by which you can nurture your students to become global citizens:
1. Foster Inclusivity in Everyday Interactions
One of the first steps in preparing students for global citizenship is cultivating an inclusive classroom culture. Inclusivity helps students develop empathy, respect, and curiosity about cultures and identities beyond their own.
How to deepen inclusivity in classrooms:
- Use classroom materials that represent diverse cultures and communities.
- Begin the year with activities that explore identity, heritage, and traditions.
- Create norms that promote kindness, active listening, and respect.
- Address stereotypes, biases, and assumptions through guided discussions.
- Use multilingual greetings, posters, and labels to celebrate linguistic diversity.
Why it matters:
Inclusive classrooms help students internalize the responsibilities of a global citizen, to respect others, build bridges, and act with fairness.
2. Discuss Global Issues in Age-Appropriate Ways
Students need exposure to global issues to understand the world they live in. Without this awareness, they cannot fully develop citizenship skills or contribute meaningfully to society.
Topics to include (adapted by age group):
- Primary: recycling, sharing resources, animal protection, kindness.
- Middle school: sustainability, water pollution, poverty, digital safety.
- High school: climate policy, global conflicts, economic inequality, media literacy.
How to make global issue discussions impactful:
- Use child-friendly news sources like Newsela or DOGO News.
- Incorporate storytelling to explain complex issues in relatable ways.
- Focus on solutions, not just problems, to avoid overwhelm.
- Encourage questions, reflections, and student-led inquiry.
Why it matters:
This builds awareness and helps students understand how to be a good global citizen. This will also make them well informed, reflective, and proactive.
3. Help Students Explore Cultures Beyond Their Own
Cultural understanding is at the heart of global citizenship. Students must learn to appreciate diversity, communicate across cultures, and develop curiosity about the world.
Ways to expand cultural exposure:
- Bring in guest speakers from diverse communities.
- Create virtual exchanges with classrooms in other countries.
- Explore global traditions, languages, cuisines, folklore, and art.
- Use storytelling to highlight similarities and differences between cultures.
- Assign research projects on global traditions or celebrations.
Practical activity:
Have students create a “Global Culture Passport”, each lesson they “visit” a new country, collect facts, reflect on insights, and stamp their passport.
Why it matters:
Exposure to global cultures enhances empathy, adaptability, and cultural intelligence, essential citizenship skills for life beyond school.
4. Nurture Humanity, Empathy & Service
Global citizenship is rooted in humanity, understanding that all people share common needs, emotions, and rights. Students must learn compassion, care for others, and the importance of contributing to their communities.
Ways to nurture humanity:
- Practice reflective journaling after discussions on global issues.
- Encourage cooperative teamwork and peer-support roles.
- Assign service-learning projects such as clean-up drives or charitable initiatives.
- Teach emotion management, active listening, and conflict resolution.
- Use books, films, and stories that highlight global human experiences.
Why it matters:
Empathy is the emotional core of global citizenship. Without it, students may understand issues but fail to act on them.
5. Build Critical Thinking Through Real-Life Scenarios
Critical thinking helps students navigate global challenges, analyze information, and make informed decisions. It is one of the most important skills in global citizenship education.
Methods to strengthen critical thinking:
- Use debates to explore multiple perspectives on global topics.
- Present news articles for analysis and bias detection.
- Run simulations like mock UN sessions or crisis-response tasks.
- Teach students to ask “why,” “how,” and “what if” questions.
- Encourage problem-solving through project-based learning.
Real-life task example:
“Your city must reduce plastic waste by 40%. Design a plan that involves schools, families, and local businesses.”
Students brainstorm, collaborate, and present their proposals — mirroring real-world problem-solving.
Why it matters:
Critical thinkers become responsible decision-makers who can respond to global complexities thoughtfully and ethically.
Encourage Students To Be Global Citizens
In this age of globalization, citizens need to collaborate their skills, knowledge, and expertise to find solutions for massive world problems. The way forward is already spelled out by NEP through the nurturing of global citizens.
Even though it is a long process and it can take ages for the traditional education system to shift to a global one, educators must be trained through offline or Online degree programs so that meet the need of the hour and shape the educational ecosystem to build responsible global citizens.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is global citizenship?
Global citizenship means understanding that we are part of an interconnected world where our actions affect others. A global citizen is someone who respects diversity, stays informed about global issues, and contributes positively to local and global communities.
2. What is the meaning of a global citizen for students?
The global citizen meaning for students includes being curious about the world, showing empathy towards others, thinking critically, appreciating cultural differences, and taking responsibility for their choices. It is about becoming aware, informed, and proactive.
3. Why is global citizenship education important in schools?
Global citizenship education helps students think globally, act responsibly, and understand world challenges such as climate change, inequality, and digital safety. It prepares them for future workplaces that require cultural intelligence, collaboration, and ethical decision-making.
4. What are the responsibilities of a global citizen?
The main responsibilities of a global citizen include:
- Respecting cultural and racial differences
- Staying informed about global issues
- Protecting the environment
- Helping others and showing empathy
- Making ethical, sustainable choices
- Speaking up for fairness and justice
5. How can teachers help in preparing students for global citizenship?
Teachers can integrate diversity discussions, global issue exploration, cultural projects, service-learning activities, and critical-thinking lessons. They can also encourage global awareness through news analysis, debates, and collaborative teamwork.
6. What citizenship skills should students develop to become global citizens?
Key citizenship skills include empathy, cultural awareness, collaboration, communication, critical thinking, problem-solving, digital literacy, and ethical reasoning. These help students thrive in multicultural environments.
7. What are some effective global citizenship activities for students?
Impactful global citizenship activities include global news circles, cultural exchange projects, mock UN, sustainability challenges, community service, cultural presentations, virtual pen-pal programs, and global issue research projects.
8. How can students learn how to be a good global citizen?
Students can learn how to be a good global citizen by practicing kindness, respecting differences, volunteering in their community, staying informed, reducing waste, thinking critically, and understanding how daily choices impact the world.
9. At what age should global citizenship be taught?
Global citizenship can be introduced as early as primary school through simple ideas like sharing, kindness, recycling, and learning about other cultures. More complex concepts—like human rights or sustainability—can be added in middle and high school.
10. Can global citizenship be taught without traveling internationally?
Absolutely. Global citizenship does not require travel. Students can become global citizens through books, digital resources, virtual exchanges, cultural storytelling, documentaries, global news, and classroom activities that connect them with the wider world.
Written By: Sanjana Chowdhury
